Android 中 Activity 是作为应用程序的载体存在,代表着一个完整的用户界面,提供了一个窗口来绘制各种视图,当 Activity 启动时,我们会通过 setContentView 方法来设置一个内容视图,这个内容视图就是用户看到的界面。
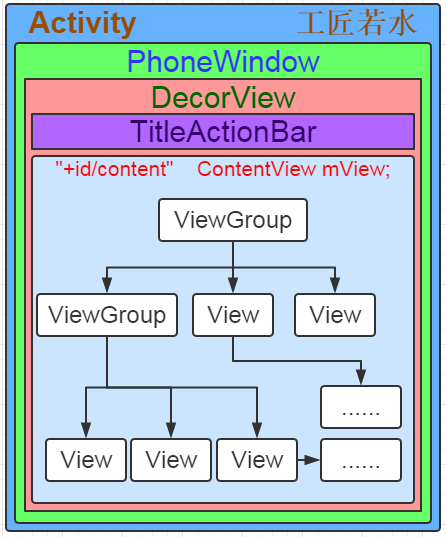
PhoneWindow 是 Android 系统中最基本的窗口系统,每个 Activity 会创建一个。PhoneWindow 是 Activity 和 View 系统交互的借口。DecorView 本质上是一个 FrameLayout,是 Activity 中所有 View 的祖先。
绘制的整体流程
当一个应用启动时,会启动一个主 Activity,Android 系统会根据 Activity 的布局来对它进行绘制。绘制会从根视图 ViewRoot 的 performTraversals() 方法开始,从上到下遍历整个视图树,每个 View 控制负责绘制自己,而 ViewGroup 还需要负责通知自己的子 View 进行绘制操作。视图操作的过程可以分为三个步骤,分别是测量(Measure)、布局(Layout)和绘制(Draw)。performTraversals 方法在类 ViewRootImpl 内,其核心代码如下。
int childWidthMeasureSpec = getRootMeasureSpec(mWidth, lp.width); int childHeightMeasureSpec = getRootMeasureSpec(mHeight, lp.height); ... // 测量 performMeasure(childWidthMeasureSpec, childHeightMeasureSpec); ... // 布局 performLayout(lp, mWidth, mHeight); ... // 绘制 performDraw();
MeasureSpec
MeasureSpec 表示的是一个 32 位的整数值,它的高 2 位表示测量模式 SpecMode,低 30 位表示某种测量模式下的规格大小 SpecSize。MeasureSpec 是 View 类的一个静态内部类,用来说明应该如何测量这个View。
三种测量模式。- UNSPECIFIED:不指定测量模式,父视图没有限制子视图的大小,子视图可以是想要的任何尺寸,通常用于系统内部,应用开发中很少使用到。
- EXACTLY:精确测量模式,当该视图的 layout_width 或者 layout_height 指定为具体数值或者 match_parent 时生效,表示父视图已经决定了子视图的精确大小,这种模式下 View 的测量值就是 SpecSize 的值。
- AT_MOST:最大值模式,当前视图的 layout_width 或者 layout_height 指定为 wrap_content 时生效,此时子视图的尺寸可以是不超过父视图运行的最大尺寸的任何尺寸。
对 DecorView 而言,它的 MeasureSpec 由窗口尺寸和其自身的 LayoutParams 共同决定;对于普通的 View,它的 MeasureSpec 由父视图的 MeasureSpec 和其本身的 LayoutParams 共同决定。
Measure
Measure 用来计算 View 的实际大小。页面的测量流程从 performMeasure 方法开始。
private void performMeasure(int childWidthMeasureSpec, int childHeightMeasureSpec) { if (mView == null) { return; } Trace.traceBegin(Trace.TRACE_TAG_VIEW, "measure"); try { mView.measure(childWidthMeasureSpec, childHeightMeasureSpec); } finally { Trace.traceEnd(Trace.TRACE_TAG_VIEW); } } 具体操作是分发给 ViewGroup 的,由 ViewGroup 在它的 measureChild 方法中传递给子 View。ViewGroup 通过遍历自身所有的子 View,并逐个调用子 View 的 measure 方法实现测量操作。
// 遍历测量 ViewGroup 中所有的 View protected void measureChildren(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) { final int size = mChildrenCount; final View[] children = mChildren; for (int i = 0; i < size; ++i) { final View child = children[i]; if ((child.mViewFlags & VISIBILITY_MASK) != GONE) { measureChild(child, widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec); } } } // 测量某个指定的 View protected void measureChild(View child, int parentWidthMeasureSpec, int parentHeightMeasureSpec) { final LayoutParams lp = child.getLayoutParams(); final int childWidthMeasureSpec = getChildMeasureSpec(parentWidthMeasureSpec, mPaddingLeft + mPaddingRight, lp.width); final int childHeightMeasureSpec = getChildMeasureSpec(parentHeightMeasureSpec, mPaddingTop + mPaddingBottom, lp.height); child.measure(childWidthMeasureSpec, childHeightMeasureSpec); } View (ViewGroup) 的 Measure 方法,最终的测量是通过回调 onMeasure 方法实现的,这个通常由 View 的特定子类自己实现,可以通过重写这个方法实现自定义 View。
public final void measure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) { ... onMeasure(widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec); .... } // 如果需要自定义测量,子类需重写这个方法 protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) { setMeasuredDimension(getDefaultSize(getSuggestedMinimumWidth(), widthMeasureSpec), getDefaultSize(getSuggestedMinimumHeight(), heightMeasureSpec)); } // 如果 View 没有重写onMeasure 方法,默认会直接调用 getDefaultSize public static int getDefaultSize(int size, int measureSpec) { int result = size; int specMode = MeasureSpec.getMode(measureSpec); int specSize = MeasureSpec.getSize(measureSpec); switch (specMode) { case MeasureSpec.UNSPECIFIED: result = size; break; case MeasureSpec.AT_MOST: case MeasureSpec.EXACTLY: result = specSize; break; } return result; } Layout
Layout 过程用来确定 View 在父容器的布局位置,他是父容器获取子 View 的位置参数后,调用子 View 的 layout 方法并将位置参数传入实现的。ViewRootImpl 的 performLayout 代码如下。
private void performLayout(WindowManager.LayoutParams lp, int desiredWindowWidth, int desiredWindowHeight) { ... host.layout(0, 0, host.getMeasuredWidth(), host.getMeasuredHeight()); ... } View 的 layout 方法代码。
public void layout(int l, int t, int r, int b) { onLayout(changed, l, t, r, b); } // 空方法,子类如果是 ViewGroup 类型,则重写这个方法,实现 ViewGroup 中所有 View 控件布局 protected void onLayout(boolean changed, int left, int top, int right, int bottom) { } Draw
Draw 操作用来将控件绘制出来,绘制的流程从 performDraw 方法开始。performDraw 方法在类 ViewRootImpl 内,其核心代码如下。
private void performDraw() { boolean canUseAsync = draw(fullRedrawNeeded); } private boolean draw(boolean fullRedrawNeeded) { ... if (!drawSoftware(surface, mAttachInfo, xOffset, yOffset, scalingRequired, dirty, surfaceInsets)) { return false; } } private boolean drawSoftware(Surface surface, AttachInfo attachInfo, int xoff, int yoff, boolean scalingRequired, Rect dirty, Rect surfaceInsets) { ... mView.draw(canvas); ... } 最终调用到每个 View 的 draw 方法绘制每个具体的 View,绘制基本上可以分为六个步骤。
public void draw(Canvas canvas) { ... // Step 1, draw the background, if needed if (!dirtyOpaque) { drawBackground(canvas); } ... // Step 2, save the canvas' layers saveCount = canvas.getSaveCount(); ... // Step 3, draw the content if (!dirtyOpaque) onDraw(canvas); // Step 4, draw the children dispatchDraw(canvas); // Step 5, draw the fade effect and restore layers canvas.drawRect(left, top, right, top + length, p); ... canvas.restoreToCount(saveCount); ... // Step 6, draw decorations (foreground, scrollbars) onDrawForeground(canvas); }